Industry
Climate solutions – Industry
Industry remains one of the most carbon-intensive and technically complex sectors to decarbonise. Sweden’s strategy combines robust policy frameworks, strategic roadmaps and cross-sector collaboration.
Long term gains to be had
Transition of the industrial sector is a challenge for any country due to high costs and slow turnover of existing infrastructure. It requires changes in investment flows, supply chains, value chains, workforce strategies, and policy frameworks. However, a shift will result in green industrial growth, boost resilience, and secure long-term economic competitiveness.
Be our industry transformation partner
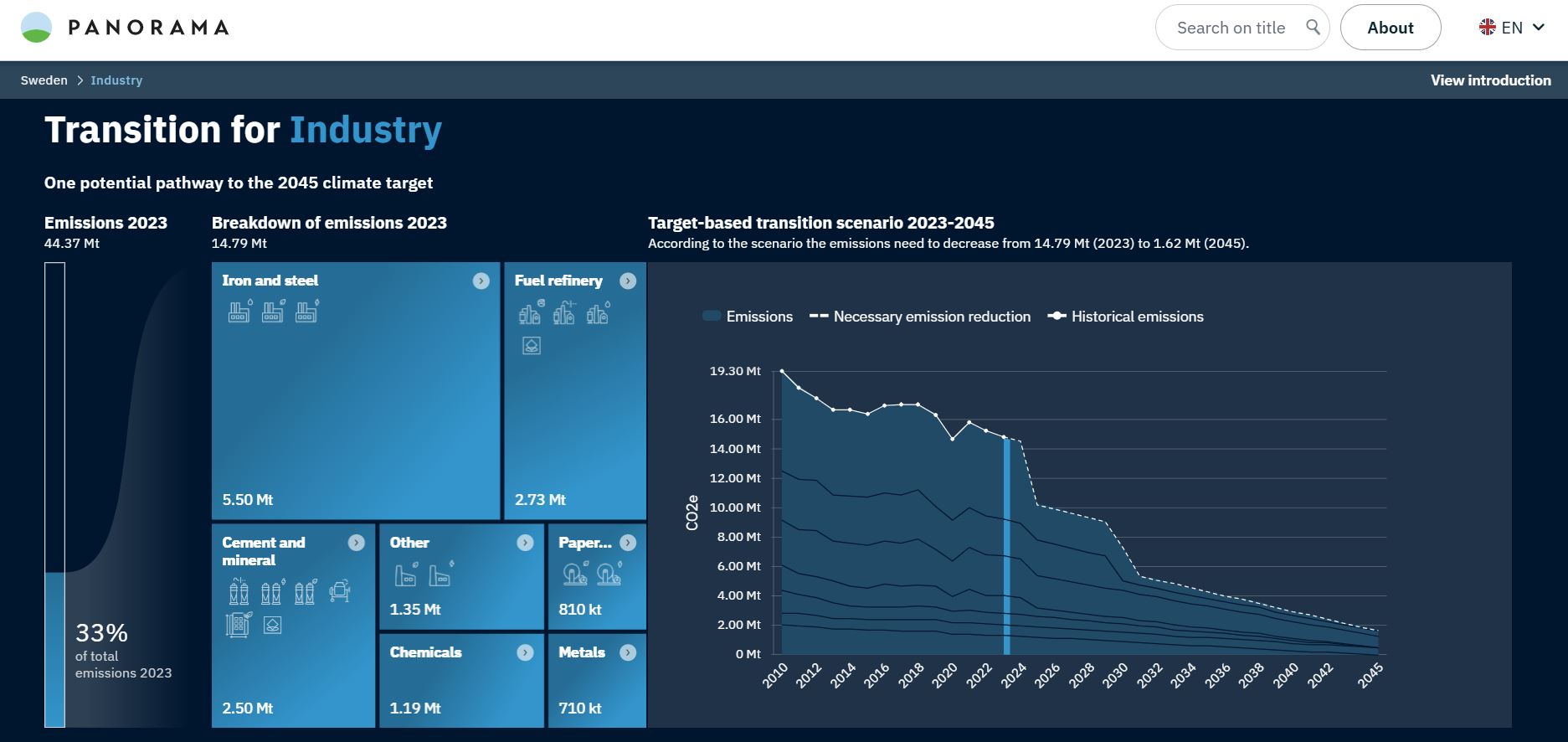
As the country with the highest number of global manufacturing companies per capita worldwide, industry is a cornerstone of Sweden’s economy. Significant reductions are needed to cut emissions by 87% by 2045, but already industrial emissions have fallen by over 24% since 2010.
Climate solutions across the board
A large and highly innovative industrial sector and prior experience on the journey towards zero emissions makes Sweden a world class partner regarding sustainable, resilient and highly competitive solutions in the industry sector. Climate solutions include:
- Circular Manufacturing by Design – Swedish firms are pioneering circular industrial processes by integrating recycled plastics, secondary raw materials, modular design, and bio-based composites. These approaches reduce dependency on virgin resources, cut lifecycle emissions, enhance supply chain resilience, lower exposure to resource price volatility, and support green job creation.
- Water and Resource Reuse – Circular systems in Sweden are enabling the reuse of treated wastewater and industrial by-products across sectors. These practices reduce water scarcity and support climate adaptation, as well as enhancing resilience in water-intensive industries.
- Demand-Side Flexibility – Swedish industry players are beginning to match energy use with grid capacity and renewable availability, reducing system strain and energy costs, and contributing to smarter, more adaptive energy use.
- Fossil-free Steel – Sweden is leading the global shift to a fossil-free steel industry. This transition to fossil-free electricity and hydrogen positions Swedish firms at the forefront of green industrial competitiveness. It reduces exposure to fossil fuel volatility and sets a precedent for decarbonising heavy industry worldwide.
- Sustainable Construction Materials – Swedish firms are developing low-carbon cement by replacing traditional clinker with fly ash, slag, and alternative binders. They also deploy bio-based and circular composites, contributing to emissions reduction and material efficiency.
- Fossil-Free Chemicals – Swedish firms are guiding the sector to pair decarbonization with defossilisation. Through electrification and efficiency and by using biomass, recycled plastics, and captured CO₂ to replace fossil-derived chemicals. This improves resource efficiency, industrial competitiveness, and reduces exposure to fossil fuel shocks. It also diversifies inputs and enhances supply chain resilience.
- Energy-Efficient Production – Swedish industry is advancing energy efficiency through audits, right-sized equipment, digital twins, predictive maintenance, and process optimisation. These tools improve competitiveness, reduce emissions, and support economic resilience by cutting operational costs.
- Waste Heat Recovery and Industrial Heat Pumps – Swedish industries capture and repurpose excess heat using high-temperature heat pumps, cutting reliance on fossil-based heating and lowering emissions. These systems support decarbonisation and improve energy security.
- Carbon Capture, Utilisation and Storage (CCUS) – Sweden is scaling up CCUS and bio-CCS to decarbonise hard-to-abate sectors such as cement, steel, and waste-to-energy. These technologies capture both fossil-based and biogenic CO₂, offering deep mitigation and long-term emissions reductions. CCUS also creates opportunities for CO₂ utilisation in products and fuels, supporting green innovation and job creation.
- Circular Economy and End-of-Life Solutions – Innovations in materials recovery, battery recycling, and remanufacturing are closing industrial resource loops. These practices extend product life, reduce waste, and lower emissions from resource extraction. They enhance resilience to supply shocks, create jobs in recycling and repair, and build more adaptive, secure industrial systems.
- Enablers to Facilitate Mitigation and Adaptation – Sweden’s public and private sectors offer a robust set of tools to support global industrial decarbonisation and adaptation, combining advanced financial mechanisms, policy expertise, cutting-edge research, and inclusive capacity-building.